Any diabetic who has incorporated regular exercise into his or her diabetes management plan knows how exercise can help to work-up a sweat. As the body muscles move more and more, the body makes an ever larger amount of heat. Both heat and movement are forms of energy, energy produced by cells in the body.
Biochemistry Of Energy Production: Any diabetic who has incorporated regular exercise into his or her diabetes management plan knows how exercise can help to work-up a sweat. As the body muscles move more and more, the body makes an ever larger amount of heat. Both heat and movement are forms of energy, energy produced by cells in the body.
The production of energy demands the presence of a fuel. Food gives the body the fuel that it needs to make energy. Carbohydrates are a prime source of energy. Fats and proteins can also be broken-down, stored and used by the body to obtain energy. The biochemistry of the body even directs the manner by which the body will make at least some of its energy. That direction opens and closes certain biochemical pathways.
The movement of voluntary muscles calls-for the availability of a ready-to-go source of energy. The body stores energy for the purpose of supplying it to muscles that are getting signals from the brain. That stored energy, potential energy, is found in a naturally-produced phosphorous compound called ADP.
When a muscle receives a signal from the brain, then muscle cells start to change molecules of ADP into ATP. The body can obtain the energy that it needs from the ATP. At the same time, the body anticipates the creation of added amounts of heat. The body appreciates the need to limit the amount of its natural energy production.
The body produces catechinpolyphenols, chemicals that can block the biochemical pathway that is used for heat production in the non-active individual. The production of heat in a non-active individual is called thermogenesis. The sort of polyphenols produced during times of muscle activity limit the ability of the body to carry-out thermogenesis.
How do the polyphenols limit the rate of thermogenesis? The polyphenols act on the fatty acids inside of the body’s fat storage cells. The cells then make the chemicals that are necessary for the production of heat.. The cells thus facilitate the movement of hydrogen ions (H*) into the cell’s mitochondria. The mitochondria help the cell to make energy.
The mitochondria do not make energy for muscle movement; they the energy that the cell uses to produce heat. The movement of H+ into the mitochondria allows the cell to bypass the biochemical pathway that is used to make ATP. Still, because it is a fat-burning process, thermogenesis requires a source of fuel (calories).
Some health professionals have sought-out foods that have high polyphenol content. According to the above information, such foods should help the body to burn fat. Recent reports indicate that green tea contains such chemicals. That is why green tea has been tooted as a way to loose weight.
Now a diabetic, more than most people, must pay attention to a second aspect of energy production. That is due to the fact that the diabetic with a well-managed diabetes control plan eats a diet with few carbohydrates. The diabetic who wants to control his or her diabetes eats lots of dairy products, and lots fruits and vegetables. The cells of the diabetic must thus obtain energy from the proteins found in those foods.
When cells use protein as an energy source, then the cells (in the course of making energy) make certain unneeded chemicals. Those unneeded chemicals can build-up in the muscles. The body must find a way to get rid of those unneeded chemicals.
The body needs to wash those chemicals out of the muscle cells. The performance of exercise initiates a rise in the movement of blood in the circulatory system. As more blood flows into the muscles, that blood then carries-away the unneeded chemicals in those muscles. An extended period of exercise washes out a larger number of chemicals.
The above fact underlines that reason why exercise should be included in a diabetes management plan. Exercise does help the body to burn energy, but exercise does even more. Exercise helps the body to deal with the biochemistry of energy production whenever the fuel for that energy comes from proteins instead of carbohydrates.
When a diabetic engages in some form of exercise, then he or she encourages the formation of more capillaries in the muscles of the body. Sometimes, the body can make up to 50% more capillaries. At the same time, the diameter of the existing capillaries increases. Blood begins to flow more quickly in those capillaries.
As the blood rushes past the muscle cells, it takes-away the unneeded chemicals in those cells. When the blood flow increase, those chemicals disappear at an ever faster rate. The blood helps to clean the muscles. Exercise enhances the rate of the blood flow. That is why diabetics need to include regular exercise in a diabetes management plan.
Exercise can also help to control hunger pangs. Diabetics understand the discomfort of hunger. Diabetics want to control their hunger, so that they are not tempted to eat foods with high carbohydrate content. Exercise can help a diabetic to reduce the number of temptations that arise from the presence of strong hunger pangs.
In that way, a diabetic can avoid the temptation to “wolf-down” his or her food. The slow digestion of food insures the slow absorption of food. The slow absorption of carbohydrates should be one goal of a diabetes management plan. That is why such a plan normally includes complex carbohydrates, as opposed to simple carbohydrates.
Bearing that fact in mind, one can better appreciate the danger of frequent visits to a fast-food restaurant. Such frequent visits should not be part of a diabetes management plan. At the same time, a diabetes management plan should provide for times spent outside of the home. A diabetic should not remain at home all day long. In that way the diabetic normally fails to obtain an adequate amount of exercise.
By understanding the biochemistry of energy production, a patent with diabetes can better fashion the sort of diabetes management plan that helps with weight control and also insures removal of any unwanted by-products from that energy production.
 This product can be confusing to some patients because while Bayer manufactures this meter you cannot buy it from the Bayer site. In most cases the actual unit is offered free of charge or at low-cost to diabetic patients while Bayer concentrates on selling models through their website that are uniquely separated from the Elite XL.
This product can be confusing to some patients because while Bayer manufactures this meter you cannot buy it from the Bayer site. In most cases the actual unit is offered free of charge or at low-cost to diabetic patients while Bayer concentrates on selling models through their website that are uniquely separated from the Elite XL.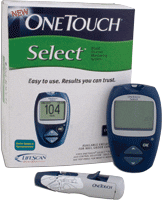 This is a fairly basic unit offered by LifeScan. It required coding, but supplies test results within 5 seconds with a minimal blood sample. It is highly regarded by physicians and often recommended for its accuracy and ease of use.
This is a fairly basic unit offered by LifeScan. It required coding, but supplies test results within 5 seconds with a minimal blood sample. It is highly regarded by physicians and often recommended for its accuracy and ease of use. The OneTouch UltraLink Glucose Meter is designed specifically for those who use the MiniMed Paradigm
The OneTouch UltraLink Glucose Meter is designed specifically for those who use the MiniMed Paradigm  Mendor, a start-up company from Finland, Europe, has developed a revolutionary Mendor
Mendor, a start-up company from Finland, Europe, has developed a revolutionary Mendor