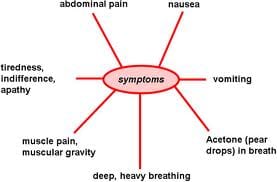
The effects of diabetes are widespread, and this chronic disease can wreak havoc on virtually every part of the body. Many diabetics are prone to eye problems such as glaucoma and cataracts. However, the most crippling eye disorder involves the retina, a phenomenon known as diabetic retinopathy.
Diabetic Retinopathy at a Glance
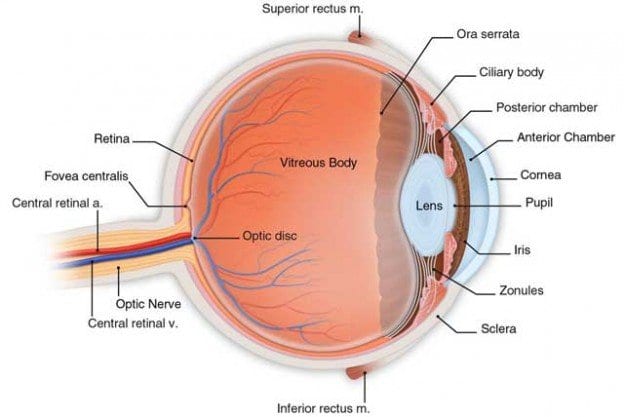
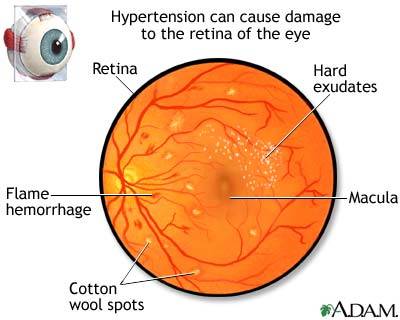
The retina is the tissue matter at the back of the eye which captures light sources and sends information to the brain. Retinopathy is used to define the damage inflicted upon the tiny capillaries that surround the retina. Individuals that have had diabetes for a significant amount of time are more likely to develop diabetic retinopathy. It is estimated that approximately 50 percent of diagnosed diabetics have been affected to some extent by this retinal disorder. Both Type I and II diabetics are at risk for developing retinopathy.
Chances of diabetic retinopathy increase with the following:
- If you are of African-American or Hispanic origin
- Have high blood pressure
- Are pregnant
- Have diabetes with uncontrolled glucose levels
When first afflicted by retinopathy, diabetics usually only experience slight changes in vision. This debilitating disorder can even progress without any noted changes in vision. However, as the condition progresses, significant eye problems can occur.
Symptoms of diabetic retinopathy include:
- Blurry vision
- Difficulty seeing at nighttime
- Floating “spiders” that obstruct vision
- Problems adjusting to changes in light
All diabetes patients should have a comprehensive eye exam with a retinopathy specialist every year to check for any precursors to the condition. Also, if you are pregnant, an eye exam should be administered immediately and then throughout your pregnancy.
Diabetic retinopathy generally occurs in two separate types: proliferative and nonproliferative.
Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (PDR)
The more advanced of the two forms, proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR) occurs when abnormal capillaries grow in the optic disc or the retina. The blood vessels can also project into the clear substance that composes the center of the eye, the vitreous. Proliferative retinopathy can result in loss of both central and peripheral vision.
Nonproliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (NPDR)
Nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy (NPDR) occurs in the early stages of the disease. The most common type of retinopathy, there are either no or extremely mild symptoms in NPDR. The process of nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy begins when the retinal capillary walls weaken. “Outpouchings,” or small protrusions known as microaneurysms stick out from the walls of the retinal blood vessels. If the microaneurysms start to leak, blood and fluid seep into the retina. Severe NPDR can result in a disorder called diabetic macular edema, the swelling of the center portion of the retina, the macula. A dysfunction in the macula can cause an obstruction in your central vision.
Treating Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetics with nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy usually do not require immediate treatment, but it is recommended that your physician keep a check on the progress of the retina. Proliferative diabetic retinopathy, however, will require surgical treatment as soon as possible. The two treatments commonly used for diabetic retinopathy are photo coagulation and vitrectomy. It must be addressed that these treatments are in no way a cure for retinopathy; they only can slow down or assist in halting the progression of the condition. Laser treatment or photo coagulation stops the leakage of blood and fluid in the retina. This is turn slows the advancement of retinopathy, and likelihood of loss of vision. In this process, a laser will attempt to seal leakage by producing tiny burns in the sections with abnormal capillaries. Photo coagulation can be performed in either a physician’s office or an outpatient surgical unit. The goal of a vitrectomy is to remove the blood and fluid engorged vitreous. The procedure begins when sections of tissue are cut and extracted from the eye. A salt solution replaces the portions that were removed, so that the pressure and shape of the eye return to normal. Recovery from vitrectomy is significantly longer than with laser treatment, and can take several weeks.