What if you knew that by adding a diabetic drug to your daily medical regimen you increased your risk of heart failure by more than 50%? Would you take the drug? One California County is taking a drug company to court to seek the removal of the drug from circulation.
According to VOAnews, “The [Santa Clara County] lawsuit was spurred by a report on the drug released by the U.S. Senate … That report accused the drug company of withholding information about side effects of serious heart problems, including death. At issue now is whether Avandia should be taken off the market.”
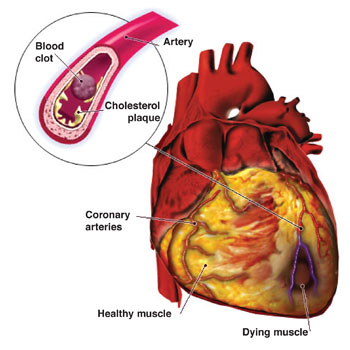
The VOAnews report stated that, “In 2007, Dr. Steven Nissen published a study showing that those taking Avandia had a 43 percent higher risk of having a heart attack and a 64 percent greater chance of dying from a heart attack than those not taking the drug. ‘We’ve been warning about this for two and a half years,’ he said. ‘There really isn’t a good reason for physicians to continue to prescribe the drug. It’s time to get it off the market.’”
Dr. Yasser Ousman at Washington Hospital Center disagrees. Ousman is quoted by VOA as saying, “There are a number of drugs that have been tested in these individuals and Avandia is one of them, and actually, it is quite effective in improving the blood sugar, in normalizing the blood sugar or delaying the occurrence of diabetes in these individuals.”
Ousman further suggests, “If you look at the large studies, that were published over the last several years, including a large number of patients comparing Avandia to a placebo or other drugs, there was actually no increase in that risk. That risk was based on smaller studies.”
Basing his findings on more than 40 clinical trials, Nissen said, “What bothers me the most is that every month that goes by, more people are harmed by a drug that people simply don’t need.”
The Food and Drug Administration have planned further review of the drug in July, but has cautioned against the discontinued use of Avandia without the advise of your primary health care provider.
The case against GlaxoSmithCline in California has to do with what is claimed as false advertising. There is the suggestion that the drug manufacturer knew the drug could cause heart issues long before they ever issued any warnings that this could be a side effect of using the medication. A Senate report even suggests that the FDA may bear some responsibility in the lack of information passed on to patients.
The VOAnews article further indicates, “A study on Avandia funded by GlaxoSmithKline published last year, found no increase in heart attacks. But it found a significant increase in the risk of heart failure where the heart cannot pump enough blood to the organs or muscles. A number of cases resulted in hospitalization or death.”
Law.com states that Santa Clara County in California “Wants the company to pay back money from all sales of Avandia in California since 1999, as well as pay restitution for medical treatment provided to Avandia users who suffered heart problems.” The county has spent around $2 million on the purchase of Avandia as part of it’s own health program over the years. The lawsuit may have been precipitated by the fact that Santa Clara County has a public hospital and the County is seeking to make decisions in the best interest of their municipal health care facility as well as the patients who use their hospital.


 Anterior Ischemic Optic
Anterior Ischemic Optic